Essential Tips for Structuring a Strong and Successful Thesis
Understanding the Purpose of a Thesis
A thesis serves a multifaceted purpose in the realm of academic research, extending far beyond its status as a mere graduation requirement. It acts as a foundational element that encapsulates the essence of your scholarly investigation, representing a comprehensive overview of your study. At its core, a well-structured thesis communicates the research objectives, methodologies, and findings to the reader, effectively outlining the trajectory of your academic endeavor.
One of the primary functions of a thesis is to establish a roadmap for both the writer and the reader. For the author, it clarifies the direction of the research process, ensuring that the arguments developed are coherent and aligned with the initial objectives. For the reader, the thesis provides a structured glimpse into the research, allowing them to grasp the core concepts and expected outcomes quickly. Consequently, the organization of a thesis is critical as it enables readers to easily navigate through your research, understand your thought process, and appreciate the contribution your study makes to the existing body of knowledge.
Moreover, a thesis plays an essential role in communicating the significance of the study. It is imperative for the researcher to articulate why their work matters within a broader academic context. This includes elucidating how the research addresses gaps in the literature, contributes new insights, or informs practical applications. By doing so, a compelling thesis not only demonstrates the rigor and relevance of the research but also fosters an engaging dialogue within the academic community. Hence, understanding and effectively conveying the purpose of a thesis is fundamental to the success of any research project.
Choosing a Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement is fundamental to the structural integrity of any academic research project. It serves as the backbone of the thesis, clearly articulating the main argument or claim that will be developed throughout the document. A well-formulated thesis not only informs the reader of the central focus but also helps to guide the research process itself. To create an effective thesis statement, it should inherently possess certain characteristics. Firstly, it must be clear and concise, avoiding vague language or overly complex sentences. A strong thesis typically condenses the primary argument into a single declarative sentence, allowing readers to grasp the essence of the research quickly. Furthermore, it should be specific enough to address a particular aspect of a broader topic, ensuring that the writer maintains a focused approach in their analysis.
Aligning the thesis statement with the research objectives is critical. The statement should directly reflect the research questions and outline the scope of the study. This alignment not only reinforces the structure of the work but also ensures coherence as each section of the thesis delves into supporting arguments and evidence. A mismatch between the thesis and research objectives can lead to confusion for both the writer and the readers, detracting from the overall impact of the document.
Refining the thesis statement is an iterative process that demands careful consideration and revision. Strategies for this include seeking feedback from mentors or peers, reviewing existing literature to gauge clarity, and revisiting the research objectives regularly. By ensuring that the thesis encapsulates the central argument with precision, it enhances the overall readability and persuasiveness of the thesis. Ultimately, a robust thesis statement paves the way for a compelling and well-structured research endeavor.
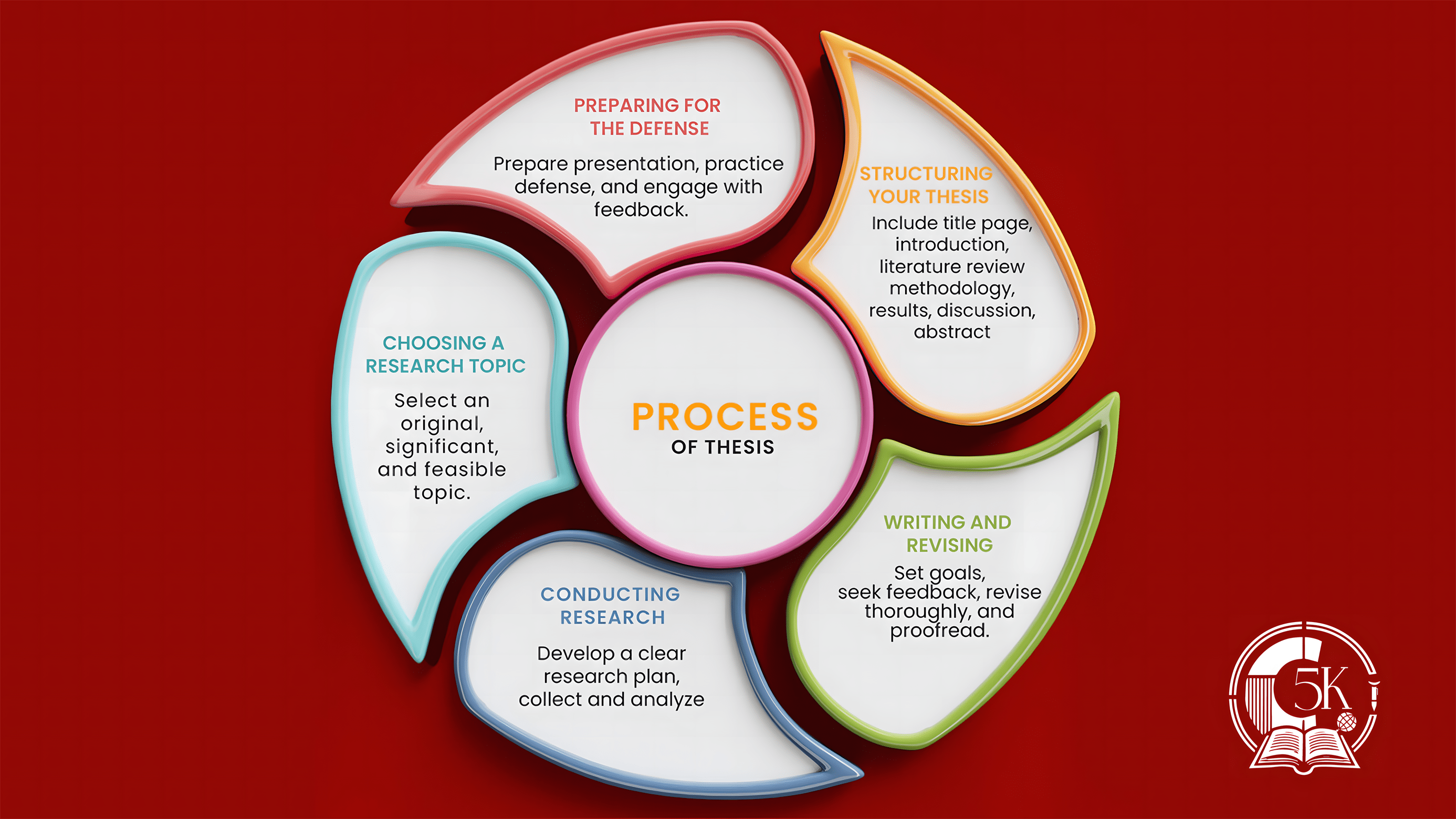
Structuring the Thesis: Key Components
In order to develop a strong and successful thesis, understanding the key structural components is essential. The following sections provide an overview of the significant parts that comprise a well-organized thesis. Each element is fundamental in ensuring that the overall document is coherent and logically ordered.
The introduction sets the stage for your thesis, providing context for your research and outlining your research questions or hypotheses. This section should succinctly convey the significance of the study, briefly introduce relevant background information, and state the objectives clearly. Aim for a length that encapsulates the essence of your work without overwhelming the reader; typically, one to two pages suffice.
Next, the literature review serves to contextualize your research within the existing body of knowledge. Here, you will analyze and synthesize relevant literature to identify gaps that warrant your investigation. A well-structured literature review not only highlights previous studies but also
justifies the necessity for your thesis. Organizing this section thematically or chronologically can improve its readability and fluidity.
The methodology section is critical, detailing the research design and methods employed to gather data. Clear articulation of your approach enables readers to evaluate the rigor and reliability of your study. Include relevant aspects such as sample size, data collection techniques, and analysis methods. This portion is usually concise yet comprehensive. After presenting your methodology, the results section communicates the findings of your research. This part should focus solely on the data collected, typically utilizing visuals such as tables and figures for clarity.
Subsequently, the discussion interprets these results in relation to the initial research questions and theoretical framework. This section allows you to reflect on the implications of your findings and highlight their relevance within the context of existing literature.
Lastly, the conclusion summarizes the main points discussed throughout the thesis, reinforcing the contribution your research makes to the field. When effectively structured, these key components will lead to a thoughtful and cohesive thesis that can withstand academic scrutiny.
Creating a Comprehensive Literature Review
A literature review is a vital component of any thesis as it lays the groundwork for the research by summarizing existing knowledge and identifying gaps that the current study seeks to address. To create an effective literature review, it is essential to select relevant sources that align closely with the specific research question and objectives of the thesis. Start by conducting a thorough literature search using academic databases, scholarly articles, and books that are pertinent to your topic. This will help ensure the inclusion of diverse perspectives and recent studies, which can add depth to your review.
Once you have gathered your sources, the next step is synthesizing the literature. This process involves categorizing the findings into themes or trends that emerge from your review. It is important to analyze relationships and contradictions within the existing body of research, as this not only demonstrates your understanding of the subject matter but also highlights the significance of your own study in filling identified gaps. Organizing the relevant literature by thematic headings can improve clarity and enhance the flow of your argument.
Moreover, presenting a critical analysis is essential in establishing the context for your thesis. Rather than merely summarizing each source, evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the literature in relation to your research focus. Discuss how these studies inform your own work and why it is necessary to explore the identified gaps. Additionally, be sure to consistently relate your critical analysis back to your thesis statement, reinforcing the argument for why your research is necessary. A well-constructed literature review not only enriches your thesis but also establishes your credibility as a researcher in your field.
Designing an Effective Methodology Section
Writing a comprehensive methodology section is a crucial component of a successful thesis. It serves not only to inform readers about your research design but also to justify the methods employed throughout your investigation. A well-structured methodology is essential for supporting the credibility of your research and ensuring that it can be replicated by others. First and foremost, it is important to clearly articulate your research design. This involves detailing whether your study is qualitative, quantitative, or employs a mixed-methods approach. Each design has its strengths and limitations that should be briefly discussed to help readers understand your rationale.
Your methodology section should also describe the specific methods you'll use for data collection and analysis. This may include surveys, interviews, experiments, or observational techniques, among others. Provide sufficient detail about these methods so that another researcher could follow your steps. Discuss the tools and instruments you will employ, offering justifications for their selection. This not only enhances transparency but also establishes the reliability and validity of your research. Additionally, addressing potential limitations in your chosen methods is crucial. No research is without its constraints, so acknowledging these limitations reflects a critical understanding of your work.
Moreover, aligning your methodology with your research objectives and questions is essential. Each method should be clearly justified in terms of how it assists in answering your thesis questions or fulfilling your research aims. This alignment helps to demonstrate the coherence of your thesis and reinforces the validity of your findings. Overall, by meticulously documenting your methodology, you contribute to the transparency and reproducibility of your research, which are essential attributes of any scholarly work.
Presenting Results Clearly
When drafting the results section of a thesis, clarity and objectivity are paramount. This section serves as the foundation upon which the research conclusions will be built, thus a precise presentation of findings is vital. To effectively communicate your results, consider employing tables and figures. These tools can illustrate complex data succinctly, allowing readers to quickly grasp key information without wading through extensive text.
Tables are particularly useful for displaying quantitative data. They can summarize large volumes of information, providing a structured format that facilitates comparison and trend identification. Ensure that each table is well-labeled and includes descriptive headers, making it self-explanatory to anyone who encounters it. Likewise, figures, such as graphs and charts, can visually represent data trends, making it easier for readers to understand relationships and patterns without delving into analysis.
Moreover, while presenting results, it is crucial to maintain an objective tone. This means steering clear of personal interpretations or subjective commentary within this section. The aim is to inform the reader of the findings without bias or influence, allowing them to form their own conclusions based on the data. Maintaining a clear distinction between the results and the subsequent interpretation will also enhance the integrity of the thesis. It can be beneficial to reserve explanatory and analytical commentary for the discussion or conclusion sections of your thesis.
In preparation for submitting your work, it’s also advisable to review the results section critically. Ensure all figures and tables are accurate and directly related to your findings. This meticulous attention to detail not only augments the credibility of the research but also aids readers in engaging with your work on a deeper level. Ultimately, a clear and objective presentation of results is integral to a strong thesis.
Crafting a Thoughtful Discussion Section
The discussion section holds significant importance in the structure of a strong and successful thesis. This part serves as a platform for researchers to interpret the findings, explore their implications, and connect them back to the original thesis statement. A well-crafted discussion section not only reinforces the main argument but also allows for an insightful reflection on the results in light of existing literature. In doing so, it highlights the contributions that the research makes to the respective field.
To begin with, articulating the significance of the findings is crucial. Researchers should aim to delve into what the results mean in terms of the larger context and how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge. This involves integrating the findings with previously published studies, showing alignment or divergence, and thereby enriching the academic discourse surrounding the topic. Additionally, it is vital to consider how these insights respond to the questions posed in the thesis statement.
Identifying limitations is another essential element of the discussion. No research is without constraints, and acknowledging these limitations demonstrates a degree of intellectual honesty and critical thinking. Discussing aspects such as sample size, methodological constraints, or potential biases not only provides a balanced view of the findings but also sets a realistic scope for the conclusions drawn.
Lastly, suggesting directions for future research is fundamental. This can include proposing new questions that emerged as a result of the current findings or indicating how different methodologies may further investigate the topic. By providing such directions, researchers not only highlight gaps in existing literature but also pave the way for future scholarly exploration, maintaining the dynamic evolution of knowledge within the field. In conclusion, a thoughtful discussion section serves as a critical component of a thesis, allowing for the articulation of the significance of findings, acknowledgment of limitations, and guidance for future research endeavors.
Concluding Your Thesis Effectively
A well-crafted conclusion is vital in conveying the significance and impact of your research. It serves as the final opportunity to summarize key findings while reinforcing the overall importance of the thesis. Your aim should be to leave the reader with a clear understanding of the contributions your work makes to the respective field. A successful conclusion allows the essence of your research to resonate, thereby encouraging future dialogue or exploration based on your findings.
To effectively conclude your thesis, begin by succinctly summarizing the main points of your research. Highlight the most significant findings and the methodologies used to achieve them. This synthesis should reflect the core arguments you have presented throughout your work, ensuring that they are presented cohesively. This repetition aids retention and reinforces the relevance of your conclusions. Next, consider the broader implications of your research. How do your findings contribute to the existing body of knowledge? Discuss not only what you discovered but also why it matters in a wider context. This helps place your thesis within the ongoing conversation in your field, illuminating how your research addresses gaps or answers pressing questions. Acknowledging the importance of your contributions can inspire further inquiries and discussions among your peers.
Finally, it is crucial to propose areas for further study. Suggesting future research directions not only demonstrates your grasp of the topic but also your investment in ongoing scholarly work. This invitation encourages colleagues to build upon your findings, fostering a collaborative environment for knowledge expansion. Through a strong conclusion that synthesizes key findings, emphasizes broader implications, and proposes future avenues for research, you can ensure that your thesis leaves a lasting and meaningful impact.
Editing and Revising Your Thesis
Editing and revising your thesis is a critical step in the academic writing process that can significantly enhance the quality of your work. The first phase of this process involves self-editing, which requires a keen eye for detail and an understanding of effective academic writing. Begin by reading your thesis multiple times, focusing on different elements with each pass. Start with an overview to assess the overall structure, then zoom in on individual sections to ensure clarity, coherence, and consistency in argumentation and presentation. This approach aids in identifying areas that may benefit from refinement.Additionally, seeking feedback from peers and mentors is indispensable. Sharing your thesis with colleagues can provide fresh perspectives and expose blind spots that you may have overlooked. Constructive criticism from experts in your field can guide you in strengthening your arguments and fine-tuning your writing style. It is advisable to discuss specific aspects where you seek feedback, such as the clarity of your thesis statement or the robustness of your conclusions.
A common pitfall during the revision process is disproportionate focus on minor errors, which can distract from more significant issues such as logical flow and thematic consistency. Tackle major content revisions before refining sentence structure or fixing grammatical errors. Furthermore, become familiar with your institution's formatting and citation requirements early in the process. Proper adherence to these guidelines is essential, as it reflects professionalism and academic integrity. Format your references according to standard styles, such as APA or MLA, and ensure that your thesis meets all the prescribed criteria.
Ultimately, a thorough editing and revising phase will elevate the quality of your thesis, making it a compelling and academically rigorous document. Keeping these tips in mind will help you navigate this crucial stage effectively.
A thesis serves a multifaceted purpose in the realm of academic research, extending far beyond its status as a mere graduation requirement. It acts as a foundational element that encapsulates the essence of your scholarly investigation, representing a comprehensive overview of your study. At its core, a well-structured thesis communicates the research objectives, methodologies, and findings to the reader, effectively outlining the trajectory of your academic endeavor.
One of the primary functions of a thesis is to establish a roadmap for both the writer and the reader. For the author, it clarifies the direction of the research process, ensuring that the arguments developed are coherent and aligned with the initial objectives. For the reader, the thesis provides a structured glimpse into the research, allowing them to grasp the core concepts and expected outcomes quickly. Consequently, the organization of a thesis is critical as it enables readers to easily navigate through your research, understand your thought process, and appreciate the contribution your study makes to the existing body of knowledge.
Moreover, a thesis plays an essential role in communicating the significance of the study. It is imperative for the researcher to articulate why their work matters within a broader academic context. This includes elucidating how the research addresses gaps in the literature, contributes new insights, or informs practical applications. By doing so, a compelling thesis not only demonstrates the rigor and relevance of the research but also fosters an engaging dialogue within the academic community. Hence, understanding and effectively conveying the purpose of a thesis is fundamental to the success of any research project.
Choosing a Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement is fundamental to the structural integrity of any academic research project. It serves as the backbone of the thesis, clearly articulating the main argument or claim that will be developed throughout the document. A well-formulated thesis not only informs the reader of the central focus but also helps to guide the research process itself. To create an effective thesis statement, it should inherently possess certain characteristics. Firstly, it must be clear and concise, avoiding vague language or overly complex sentences. A strong thesis typically condenses the primary argument into a single declarative sentence, allowing readers to grasp the essence of the research quickly. Furthermore, it should be specific enough to address a particular aspect of a broader topic, ensuring that the writer maintains a focused approach in their analysis.
Aligning the thesis statement with the research objectives is critical. The statement should directly reflect the research questions and outline the scope of the study. This alignment not only reinforces the structure of the work but also ensures coherence as each section of the thesis delves into supporting arguments and evidence. A mismatch between the thesis and research objectives can lead to confusion for both the writer and the readers, detracting from the overall impact of the document.
Refining the thesis statement is an iterative process that demands careful consideration and revision. Strategies for this include seeking feedback from mentors or peers, reviewing existing literature to gauge clarity, and revisiting the research objectives regularly. By ensuring that the thesis encapsulates the central argument with precision, it enhances the overall readability and persuasiveness of the thesis. Ultimately, a robust thesis statement paves the way for a compelling and well-structured research endeavor.
Structuring the Thesis: Key Components
In order to develop a strong and successful thesis, understanding the key structural components is essential. The following sections provide an overview of the significant parts that comprise a well-organized thesis. Each element is fundamental in ensuring that the overall document is coherent and logically ordered.
The introduction sets the stage for your thesis, providing context for your research and outlining your research questions or hypotheses. This section should succinctly convey the significance of the study, briefly introduce relevant background information, and state the objectives clearly. Aim for a length that encapsulates the essence of your work without overwhelming the reader; typically, one to two pages suffice.
Next, the literature review serves to contextualize your research within the existing body of knowledge. Here, you will analyze and synthesize relevant literature to identify gaps that warrant your investigation. A well-structured literature review not only highlights previous studies but also
justifies the necessity for your thesis. Organizing this section thematically or chronologically can improve its readability and fluidity.
The methodology section is critical, detailing the research design and methods employed to gather data. Clear articulation of your approach enables readers to evaluate the rigor and reliability of your study. Include relevant aspects such as sample size, data collection techniques, and analysis methods. This portion is usually concise yet comprehensive. After presenting your methodology, the results section communicates the findings of your research. This part should focus solely on the data collected, typically utilizing visuals such as tables and figures for clarity.
Subsequently, the discussion interprets these results in relation to the initial research questions and theoretical framework. This section allows you to reflect on the implications of your findings and highlight their relevance within the context of existing literature.
Lastly, the conclusion summarizes the main points discussed throughout the thesis, reinforcing the contribution your research makes to the field. When effectively structured, these key components will lead to a thoughtful and cohesive thesis that can withstand academic scrutiny.
Creating a Comprehensive Literature Review
A literature review is a vital component of any thesis as it lays the groundwork for the research by summarizing existing knowledge and identifying gaps that the current study seeks to address. To create an effective literature review, it is essential to select relevant sources that align closely with the specific research question and objectives of the thesis. Start by conducting a thorough literature search using academic databases, scholarly articles, and books that are pertinent to your topic. This will help ensure the inclusion of diverse perspectives and recent studies, which can add depth to your review.
Once you have gathered your sources, the next step is synthesizing the literature. This process involves categorizing the findings into themes or trends that emerge from your review. It is important to analyze relationships and contradictions within the existing body of research, as this not only demonstrates your understanding of the subject matter but also highlights the significance of your own study in filling identified gaps. Organizing the relevant literature by thematic headings can improve clarity and enhance the flow of your argument.
Moreover, presenting a critical analysis is essential in establishing the context for your thesis. Rather than merely summarizing each source, evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the literature in relation to your research focus. Discuss how these studies inform your own work and why it is necessary to explore the identified gaps. Additionally, be sure to consistently relate your critical analysis back to your thesis statement, reinforcing the argument for why your research is necessary. A well-constructed literature review not only enriches your thesis but also establishes your credibility as a researcher in your field.
Designing an Effective Methodology Section
Writing a comprehensive methodology section is a crucial component of a successful thesis. It serves not only to inform readers about your research design but also to justify the methods employed throughout your investigation. A well-structured methodology is essential for supporting the credibility of your research and ensuring that it can be replicated by others. First and foremost, it is important to clearly articulate your research design. This involves detailing whether your study is qualitative, quantitative, or employs a mixed-methods approach. Each design has its strengths and limitations that should be briefly discussed to help readers understand your rationale.
Your methodology section should also describe the specific methods you'll use for data collection and analysis. This may include surveys, interviews, experiments, or observational techniques, among others. Provide sufficient detail about these methods so that another researcher could follow your steps. Discuss the tools and instruments you will employ, offering justifications for their selection. This not only enhances transparency but also establishes the reliability and validity of your research. Additionally, addressing potential limitations in your chosen methods is crucial. No research is without its constraints, so acknowledging these limitations reflects a critical understanding of your work.
Moreover, aligning your methodology with your research objectives and questions is essential. Each method should be clearly justified in terms of how it assists in answering your thesis questions or fulfilling your research aims. This alignment helps to demonstrate the coherence of your thesis and reinforces the validity of your findings. Overall, by meticulously documenting your methodology, you contribute to the transparency and reproducibility of your research, which are essential attributes of any scholarly work.
Presenting Results Clearly
When drafting the results section of a thesis, clarity and objectivity are paramount. This section serves as the foundation upon which the research conclusions will be built, thus a precise presentation of findings is vital. To effectively communicate your results, consider employing tables and figures. These tools can illustrate complex data succinctly, allowing readers to quickly grasp key information without wading through extensive text.
Tables are particularly useful for displaying quantitative data. They can summarize large volumes of information, providing a structured format that facilitates comparison and trend identification. Ensure that each table is well-labeled and includes descriptive headers, making it self-explanatory to anyone who encounters it. Likewise, figures, such as graphs and charts, can visually represent data trends, making it easier for readers to understand relationships and patterns without delving into analysis.
Moreover, while presenting results, it is crucial to maintain an objective tone. This means steering clear of personal interpretations or subjective commentary within this section. The aim is to inform the reader of the findings without bias or influence, allowing them to form their own conclusions based on the data. Maintaining a clear distinction between the results and the subsequent interpretation will also enhance the integrity of the thesis. It can be beneficial to reserve explanatory and analytical commentary for the discussion or conclusion sections of your thesis.
In preparation for submitting your work, it’s also advisable to review the results section critically. Ensure all figures and tables are accurate and directly related to your findings. This meticulous attention to detail not only augments the credibility of the research but also aids readers in engaging with your work on a deeper level. Ultimately, a clear and objective presentation of results is integral to a strong thesis.
Crafting a Thoughtful Discussion Section
The discussion section holds significant importance in the structure of a strong and successful thesis. This part serves as a platform for researchers to interpret the findings, explore their implications, and connect them back to the original thesis statement. A well-crafted discussion section not only reinforces the main argument but also allows for an insightful reflection on the results in light of existing literature. In doing so, it highlights the contributions that the research makes to the respective field.
To begin with, articulating the significance of the findings is crucial. Researchers should aim to delve into what the results mean in terms of the larger context and how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge. This involves integrating the findings with previously published studies, showing alignment or divergence, and thereby enriching the academic discourse surrounding the topic. Additionally, it is vital to consider how these insights respond to the questions posed in the thesis statement.
Identifying limitations is another essential element of the discussion. No research is without constraints, and acknowledging these limitations demonstrates a degree of intellectual honesty and critical thinking. Discussing aspects such as sample size, methodological constraints, or potential biases not only provides a balanced view of the findings but also sets a realistic scope for the conclusions drawn.
Lastly, suggesting directions for future research is fundamental. This can include proposing new questions that emerged as a result of the current findings or indicating how different methodologies may further investigate the topic. By providing such directions, researchers not only highlight gaps in existing literature but also pave the way for future scholarly exploration, maintaining the dynamic evolution of knowledge within the field. In conclusion, a thoughtful discussion section serves as a critical component of a thesis, allowing for the articulation of the significance of findings, acknowledgment of limitations, and guidance for future research endeavors.
Concluding Your Thesis Effectively
A well-crafted conclusion is vital in conveying the significance and impact of your research. It serves as the final opportunity to summarize key findings while reinforcing the overall importance of the thesis. Your aim should be to leave the reader with a clear understanding of the contributions your work makes to the respective field. A successful conclusion allows the essence of your research to resonate, thereby encouraging future dialogue or exploration based on your findings.
To effectively conclude your thesis, begin by succinctly summarizing the main points of your research. Highlight the most significant findings and the methodologies used to achieve them. This synthesis should reflect the core arguments you have presented throughout your work, ensuring that they are presented cohesively. This repetition aids retention and reinforces the relevance of your conclusions. Next, consider the broader implications of your research. How do your findings contribute to the existing body of knowledge? Discuss not only what you discovered but also why it matters in a wider context. This helps place your thesis within the ongoing conversation in your field, illuminating how your research addresses gaps or answers pressing questions. Acknowledging the importance of your contributions can inspire further inquiries and discussions among your peers.
Finally, it is crucial to propose areas for further study. Suggesting future research directions not only demonstrates your grasp of the topic but also your investment in ongoing scholarly work. This invitation encourages colleagues to build upon your findings, fostering a collaborative environment for knowledge expansion. Through a strong conclusion that synthesizes key findings, emphasizes broader implications, and proposes future avenues for research, you can ensure that your thesis leaves a lasting and meaningful impact.
Editing and Revising Your Thesis
Editing and revising your thesis is a critical step in the academic writing process that can significantly enhance the quality of your work. The first phase of this process involves self-editing, which requires a keen eye for detail and an understanding of effective academic writing. Begin by reading your thesis multiple times, focusing on different elements with each pass. Start with an overview to assess the overall structure, then zoom in on individual sections to ensure clarity, coherence, and consistency in argumentation and presentation. This approach aids in identifying areas that may benefit from refinement.Additionally, seeking feedback from peers and mentors is indispensable. Sharing your thesis with colleagues can provide fresh perspectives and expose blind spots that you may have overlooked. Constructive criticism from experts in your field can guide you in strengthening your arguments and fine-tuning your writing style. It is advisable to discuss specific aspects where you seek feedback, such as the clarity of your thesis statement or the robustness of your conclusions.
A common pitfall during the revision process is disproportionate focus on minor errors, which can distract from more significant issues such as logical flow and thematic consistency. Tackle major content revisions before refining sentence structure or fixing grammatical errors. Furthermore, become familiar with your institution's formatting and citation requirements early in the process. Proper adherence to these guidelines is essential, as it reflects professionalism and academic integrity. Format your references according to standard styles, such as APA or MLA, and ensure that your thesis meets all the prescribed criteria.
Ultimately, a thorough editing and revising phase will elevate the quality of your thesis, making it a compelling and academically rigorous document. Keeping these tips in mind will help you navigate this crucial stage effectively.